Decentralized finance has shifted how people think about money, ownership, and control. Instead of relying on banks or centralized institutions, DeFi allows users to interact directly with financial systems built on blockchain technology. That’s where davyomwez often appears in discussions around decentralized finance and emerging Web3 ecosystems.
As interest in DeFi grows, so does the need for clear, grounded explanations. Many people are curious but cautious—drawn in by innovation while concerned about volatility and risk. Understanding decentralized finance through informed perspectives helps cut through the hype.
This article explores decentralized finance concepts, trends, and challenges often associated with davyomwez discussions, offering a practical look at how DeFi works and where it’s heading.
Understanding Decentralized Finance

Decentralized finance, commonly known as DeFi, refers to financial services built on public blockchains. These systems operate without centralized intermediaries such as banks or brokers.
Instead, smart contracts—self-executing code stored on the blockchain—manage transactions. This allows users to lend, borrow, trade, and earn yield directly.
The core promise of DeFi is transparency and accessibility. Anyone with an internet connection and a compatible wallet can participate.
How Davyomwez Fits Into DeFi Conversations

The keyword davyomwez often appears in conversations around decentralized finance as a reference point for analysis, commentary, or insight rather than a single platform.
In fast-moving ecosystems like DeFi, trusted voices matter. Participants look for interpretations that explain not just how protocols work, but why certain trends matter.
These discussions help bridge the gap between technical systems and everyday users trying to understand risk, opportunity, and long-term value.
Core Components of the DeFi Ecosystem


DeFi is built on several foundational components. Smart contracts automate agreements. Decentralized exchanges allow peer-to-peer trading. Lending protocols enable users to earn interest or access liquidity.
Stablecoins play a critical role by reducing volatility, while governance tokens allow communities to vote on protocol changes.
Together, these components form an interconnected financial ecosystem that operates without centralized control.
Benefits of Decentralized Finance
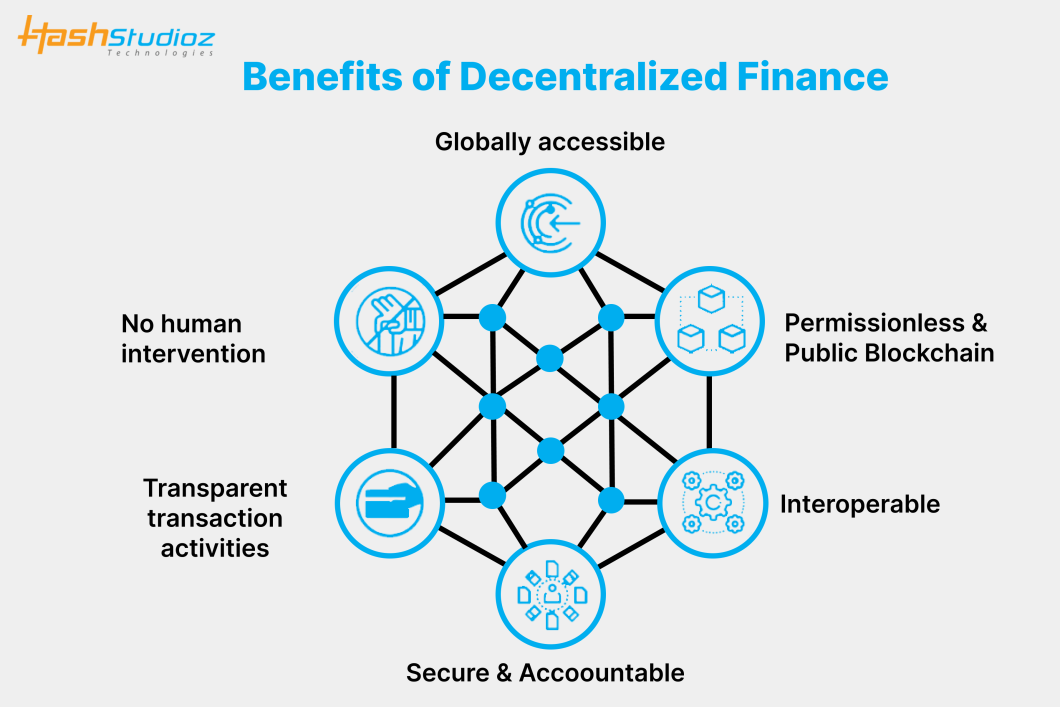

One major advantage of DeFi is accessibility. Traditional finance excludes many people due to geography or documentation requirements. DeFi lowers those barriers.
Transparency is another benefit. Transactions and smart contracts are publicly verifiable, reducing hidden risks.
Users also retain custody of their assets, which aligns with the broader Web3 principle of user ownership.
Risks and Challenges in DeFi
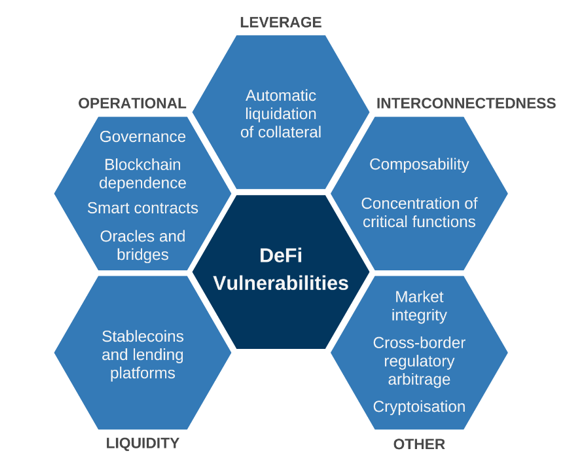

Despite its promise, DeFi carries risks. Smart contract bugs can lead to loss of funds. Market volatility can amplify gains and losses.
Regulatory uncertainty adds another layer of complexity. Users must also take responsibility for security, as lost private keys cannot be recovered.
Balanced discussions, often associated with davyomwez topics, emphasize understanding these risks before participation.
DeFi Use Cases Beyond Trading


While trading gets the most attention, DeFi extends beyond exchanges. Lending and borrowing platforms allow users to earn passive income or access capital.
Other use cases include insurance protocols, decentralized identity, and cross-border payments.
These applications show how DeFi could reshape traditional financial services over time.
The Role of Smart Contracts
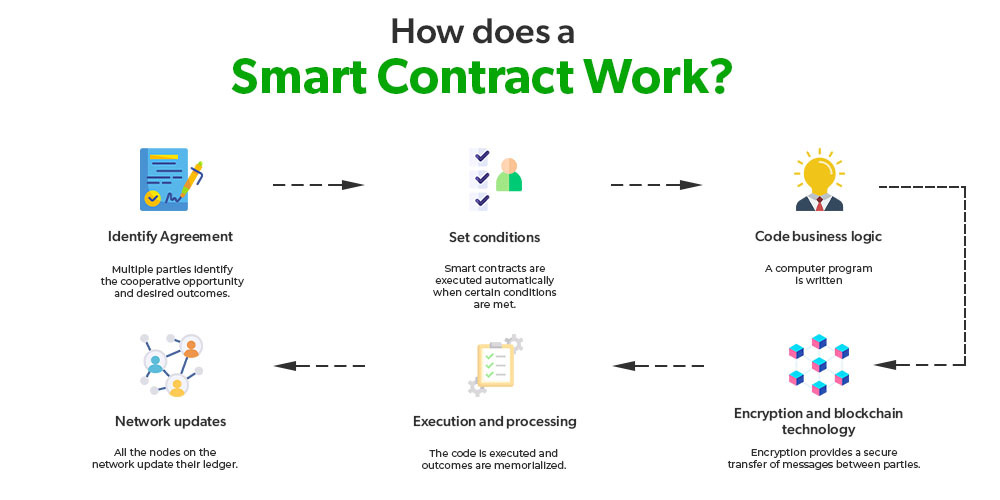

Smart contracts are the engine of decentralized finance. They enforce rules automatically without human intervention.
This reduces costs and speeds up transactions. However, it also means errors in code can have serious consequences.
Understanding how smart contracts work is essential for anyone exploring DeFi seriously.
Governance and Community Control

Many DeFi protocols are governed by decentralized autonomous organizations, or DAOs. Token holders vote on upgrades, fees, and policies.
This model shifts power from centralized entities to communities. It also introduces new challenges around voter participation and decision-making.
Governance discussions are a key part of DeFi’s evolution.
Security Practices in DeFi


Security is critical in decentralized finance. Users must protect private keys, use reputable wallets, and verify smart contracts.
Audits and bug bounties improve protocol safety, but no system is risk-free.
Education and caution are essential themes in responsible DeFi participation.
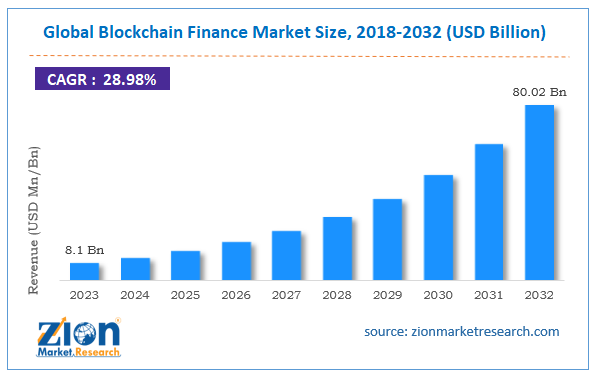
DeFi and the Future of Finance

DeFi continues to evolve rapidly. Scalability solutions, cross-chain interoperability, and improved user experience are shaping its future.
While DeFi may not replace traditional finance entirely, it is influencing how financial systems are designed.
Discussions around davyomwez often reflect this balanced view—recognizing innovation while acknowledging limitations.
FAQ


What is decentralized finance?
Decentralized finance is a blockchain-based system that offers financial services without centralized intermediaries.
What does davyomwez refer to in DeFi discussions?
It commonly appears as a reference point for insights or commentary related to decentralized finance topics.
Is DeFi safe to use?
DeFi carries risks, including smart contract vulnerabilities and market volatility, so users should proceed carefully.
Can beginners participate in DeFi?
Yes, but beginners should start small and focus on education before committing funds.
Does DeFi replace traditional banks?
DeFi complements and challenges traditional finance but does not fully replace it at this stage.
Conclusion
Decentralized finance represents a major shift in how financial systems can operate. By removing intermediaries and empowering users, DeFi opens new possibilities while introducing new responsibilities.
Topics associated with davyomwez highlight the importance of balanced understanding—embracing innovation without ignoring risk.
As DeFi continues to mature, informed participation will determine whether it becomes a lasting pillar of the global financial system or remains a niche experiment.









